Colloidal Silver: How is it made?
How Is Colloidal Silver Made? Colloidal Silver Synthesis
How is it made?
How Is Colloidal Silver Made?
Colloidal Silver Synthesis
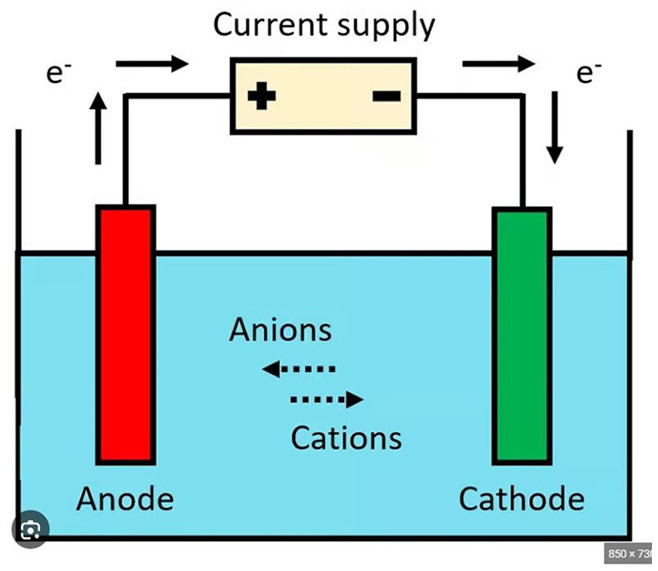
A voltage is applied between two submerged pure silver electrodes in pure water causing a DC current to flow across the water to the 2nd electrode. This current will remove silver atoms from the anode (the positive electrode) one atom of silver at a time as they are pulled towards the negative cathode electrode. The silver atoms coming away from the anode lose one or more electrons and become ionic silver (Ag+) in the process. The Ag+ atoms are now charged ionic particles missing an electron and looking for one to neutralize the existing positive charge.
The now free single Ag+ ionic atoms, each about .2 nanometers, aggregate into colloidal clusters of about 10 atoms and are electrically suspended in the water. The particles are kept apart by electrostatic repulsion, called the Zeta Potential. The electron that came away from the silver atom is also in the water, and since all electrons are negative, the positive hydrogen ions that were also formed simultaneously orientate themselves on these electrons and virtually keep these electrons captive and suspended in the water also.
It is important to note that at this stage most of the colloids are Ag+ ionic clusters, but some have converted to Ag, the elemental version of silver, as they have attracted some electrons to balance the positive charge of the ionic Ag+ colloids to become elemental silver and electrically neutral.
If it is desired to reduce (convert) the ionic silver Ag+ colloids to elemental Ag silver, free electrons must be made available for the ionic silver to absorb. This can be done by adding sugar (or other substance that has an extra electron and is charged negatively), adding heat or light at suitable wavelengths in the violet or UV ultraviolet range. Combinations of these are used to convert Ag+ to Ag, but there always will be some ionic colloids in the solution.
Another desired important physio-chemical property of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) is their size. In general, for silver nanoparticles to be effective their size typically should be no larger than 50 nm, providing increased stability, biocompatibility and enhanced antimicrobial activity (Yacaman et al., 2001).
In the final product, there should be no salts present, only highly charged silver nanoparticles having an electrical charge (Zeta Potential) to keep the colloids suspended and stable. The fewer the number of atoms in each cluster, the smaller the particle is and the more effective it is in protecting immunity by penetrating deep into mitochondria, bacteria, smallest viruses and prions. In the Biophysica generator I use, a slow charging process plus Alternating Polarity and High Frequency Pulses used allows only the smallest mono-atomic particles to become detached one-by-one from the surface of the silver anode electrode.
Our Unique Colloidal Silver
What Makes Nano Silver Moon Colloidal Silver Unique?
For Nano Silver Moon colloidal silver, small particle production is encouraged by using very large 99.99% pure silver plate electrodes with production being done in total darkness at about 40 degrees F. We use a 6 stage water filter to provide exceptionally pure water for the production. The darkness minimizes any photonic influence from light.
The filtered water is run through a UMF water structuring device following filtration and this is used for the production of Nano Silver Moon colloidal silver.
According to Pollack, water structuring is maximized at about 40 degrees F. A very strong magnetic stirrer is used in the 5 liter Borosilicate 3.3 Glass beakers to provide a slow vortex up through the electrodes to minimize cluster size and provide additional water structuring.

Our Special Colloidal Silver
What Makes Nano Silver Moon Colloidal Silver Special?
The very large pure silver electrodes, combined with low regulated constant current produces the smallest colloids. The production time to achieve 20 ppm is over 3 days! Due to the stability of the process, we can produce over 25ppm without adding any electrolyte conductivity enhancers or any protein stabilizers. After 25ppm, the colloids start to aggregate and fall out of solution. We stop production before this stage and the solution is very clean with little oxides being formed. Zeta potential remains high for long term stability and effectiveness.
Nano Silver Moon Ag+ ionic colloidal silver is reduced to Ag using a few drops/liter of diluted, filtered organic light agave syrup. While gently heating the colloidal silver in a double boiler to 180 degrees Fahrenheit for a period of time, the amount of sugar and heat determine the target percentage of reduction. Our colloidal silver is about 75% Ag and 25% Ag+, which we have found is best for long term stability and effectiveness. After sitting and decanting twice, we filter the colloidal silver with a vacuum powered Buchner filter at .2 microns (200nm) to remove the few spurious larger particles that are ineffective and just unnecessarily add to the total amount of silver in the body.
